Have you ever wondered how to protect your cells against the challenges of modern life? The answer may lie in one of the most powerful concepts in nutrition.
Antioxidants
These small but powerful molecules are heroes in the fight against free radicals and play a crucial role in protecting our cells from damage. But what exactly do antioxidants do in our bodies? Can they actually slow down cell aging? This article dives deep into the world of antioxidants and explains how they can support our health – along with an overview of the best foods rich in these valuable nutrients.
If we leave out an apple that’s been cut, it turns brown after a short time. Chemists call this process oxidation. The apple’s enzymes and polyphenols (certain phytonutrients) react with the oxygen in the air, making it turn brown. But there’s a simple trick to prevent this: lemon juice. Some might drizzle lemon juice over fruit salad, for example, to keep it looking fresh and appetizing for a longer period of time. That works because lemon juice contains vitamin C, which is an antioxidant.

How Does Oxidative Stress Develop?
Just as in the example of the apple, the natural protective effect of antioxidants also works in the cell. Since the entire body is made up of individual cells, our cellular health is the basis for us staying well and not getting sick.
Free Radicals through Metabolic Processes
A lot of metabolic processes take place in the body around the clock: we breathe, move, and digest our meals. This causes the formation of by-products called free radicals, which trigger unfavorable chain reactions and can damage the cell. That being said, it’s not necessary or even possible to completely prevent the formation of free radicals in the body – as long as there’s a balanced ratio of both antioxidants and free radicals. This is because antioxidants deactivate free radicals and prevent them from harming the cell, which is why they’re also called radical scavengers.
Free Radicals Due to External Factors
If the ratio is unbalanced, meaning there are too many free radicals in the body with not enough antioxidants, this causes something called oxidative stress. This is often a result of a diet low in antioxidants combined with high external stress, because free radicals are not only created by internal processes, but are also promoted by harmful external influences.
Influences Promoting Free Radicals:
- Nicotine and cigarette smoke
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Unhealthy diet, which contains many additives, among other things
- Physical and psychological stress
- Inflammatory processes in the body
- Environmental toxins like lead, cadmium, mercury, ozone
- Radioactive and ionizing radiation, for example from a smartphone or computer
Free radicals are created both by natural processes in the body and by harmful factors from outside, like smoking, environmental toxins, or an unhealthy diet.

What Are the Effects of Oxidative Stress?
If there are too many free radicals in the body, they can destroy cell components like DNA, receptors, and the outer cell membrane. Additionally, they cause the body’s own repair mechanisms to no longer function properly in repairing the damaged cells.
Promotes Disease
Oxidative stress does not directly cause disease in its own right, but it does put the body in an imbalance that can contribute to the development of a number of diseases. Numerous studies have demonstrated a link between oxidative stress and diseases like atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease (1), Parkinson’s disease (2) and cancer (3).
Non-Specific First Symptoms
Initial signs of oxidative stress could be manifested by a variety of symptoms, like fatigue, lack of concentration, tendency to inflammation, susceptibility to infections, premature aging of the skin, and disturbances in hormone balance. Here’s the problem: Since the symptoms are very unspecific, it’s often difficult to get to the bottom of them. Some people whose cells suffer from oxidative stress also don’t notice any symptoms until diseases start to develop.
Oxidative stress can initially manifest itself through symptoms like exhaustion, susceptibility to infections, and lack of concentration. As a result, various diseases can develop.

How Do Antioxidants Work?
Antioxidants can help the body fight free radicals. This is because they have an excess of electrons and are able to donate an electron (-) to neutralize oxidants (free radicals +), thus interrupting the chain reaction of free radicals.
Antioxidants can thus protect our cells by interrupting the chain reaction of free radicals. Through this property, they delay or inhibit the occurrence of cell damage. Recent research indicates that antioxidants can even positively influence life expectancy by slowing down aging processes (4).
Are you interested in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the health benefits of a plant-based diet? Download the curriculum for our Holistic Nutrition Coach training program.
What Are the Different Types of Antioxidants?
There are a number of substances that have an antioxidant effect. They can be found in food or can be produced by the body itself.
Endogenous Antioxidants
Glutathione is one of the most important endogenous antioxidants. The sulfur-containing protein not only protects cells, but also helps convert the antioxidant vitamin C back to its active form after it inactivates a free radical. A healthy diet, as well as regular exercise and sports adapted to individual fitness level, all promote the formation of glutathione in the liver.
Antioxidants in Food
Antioxidant substances in foods include vitamins, trace elements, and phytonutrients.
Carotenoids: The plant pigment beta-carotene belongs to the group of carotenoids. With its bright color, it’s found in carrots, pumpkins, tomatoes, and peppers, among other things. Here’s a little known fact: Beta-carotene is also found in green vegetables like spinach and kale. Carotenoids also include lycopene from tomatoes and astaxanthin from green algae.
Polyphenols: This group also belongs to phytonutrients. Polyphenols include resveratrol (found in dark grapes), anthocyanins (found in blueberries and the aronia berries), and oligomeric proanthocyanidins, or OPC for short (found in dark grapes). Various polyphenols also provide the bitter taste in coffee, black and green tea, and cocoa. Additionally, they’re found primarily in red and purple fruits and vegetables, like cherries, blackberries, and red cabbage. Nuts like walnuts and hazelnuts also contain antioxidant substances.
Sulfides: These are responsible for the strong smell of garlic, onions, and leeks. The healthy phytonutrients not only have antioxidant properties, but also anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
Phytoestrogens: These substances, also known as plant hormones, are found in soy, flaxseed, Brussels sprouts, and kohlrabi, to give some examples. Studies have shown that phytoestrogens reduce symptoms in menopausal women (5). but whether a particularly high consumption can promote breast cancer is still being researched.
Selenium: One to two Brazil nuts per day will cover the body’s selenium requirement. This trace element not only has an antioxidant effect, but also plays an important role keeping the immune system intact. In addition to Brazil nuts, selenium is found in broccoli and lentils.
Zinc: This trace mineral also scavenges free radicals, protecting cellular health. Zinc is found in foods like pumpkin seeds, oatmeal, and legumes.
Vitamin C: This vitamin is found in all fruits and vegetables, some popular examples are peppers, berries, broccoli, and spinach.
Vitamin E: This fat-soluble vitamin is mainly found in oils like flaxseed oil, rapeseed oil, and olive oil. It’s also present in avocados, peanuts, and hazelnuts.
Which Foods Are Particularly Rich in Antioxidants?
It’s impossible for those who eat a raw vegan diet to have a lack of antioxidants. There are often multiple antioxidant substances in most plant foods.
These food groups are particularly rich in antioxidants:
- Wild plants
- Leafy salads
- Vegetables
- Berries and fruits
- Spices
- Sprouts
- Microgreens
Those who rely on a raw vegan diet automatically take in lots of antioxidants, protecting their cells. Other tips: Buy organic quality food, eat it as fresh as possible, and prepare it gently.
Maja Biel (Author)
Ecotrophologist, food journalist and nutritionist. Maja has her own practice and supports Your Nutrition Academy with her expertise.
Tips for practical implementation:

👉 From now on, prefer colorful foods
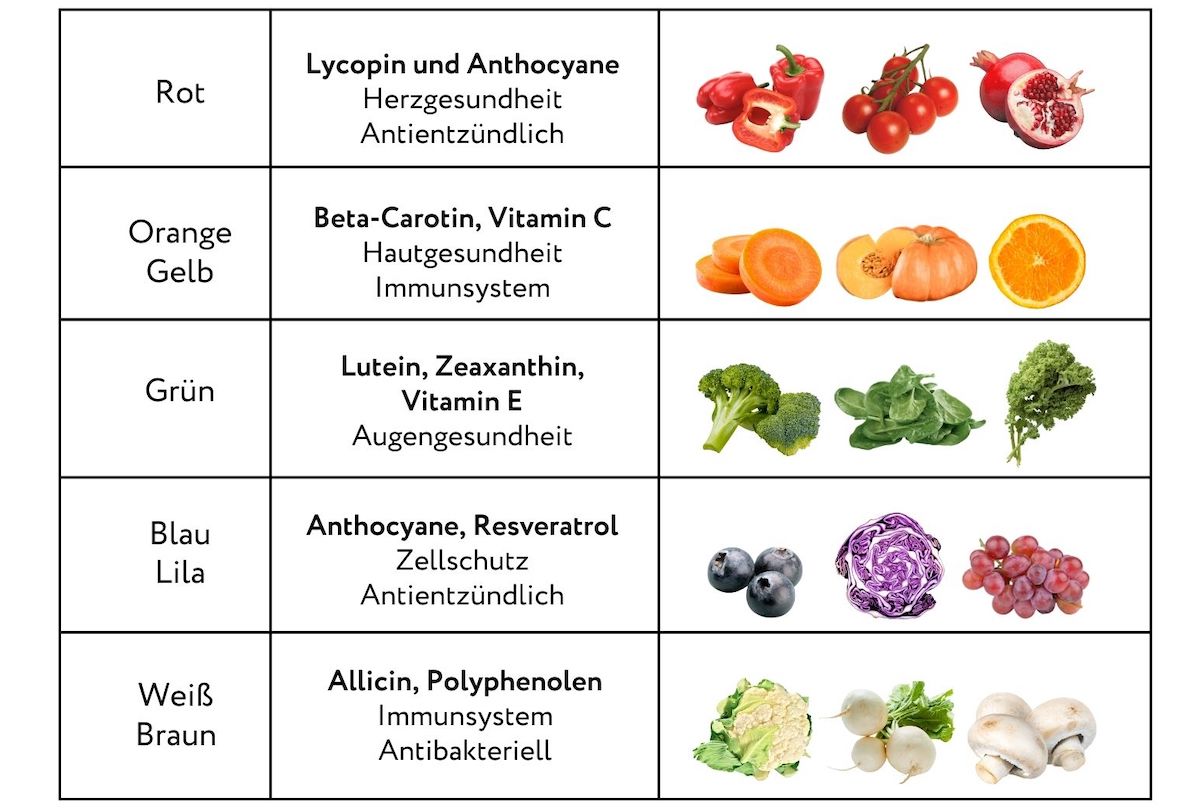
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue and purple – each color brings with it different nutrients and antioxidants that can fight inflammation, strengthen the immune system and slow down the aging process. From lycopene in tomatoes to anthocyanins in blueberries: the variety and power of these nutrients should not be underestimated.
Colorful foods and their antioxidants:
Turmeric Ginger Shot
Turmeric and ginger both have a strong antioxidant effect.
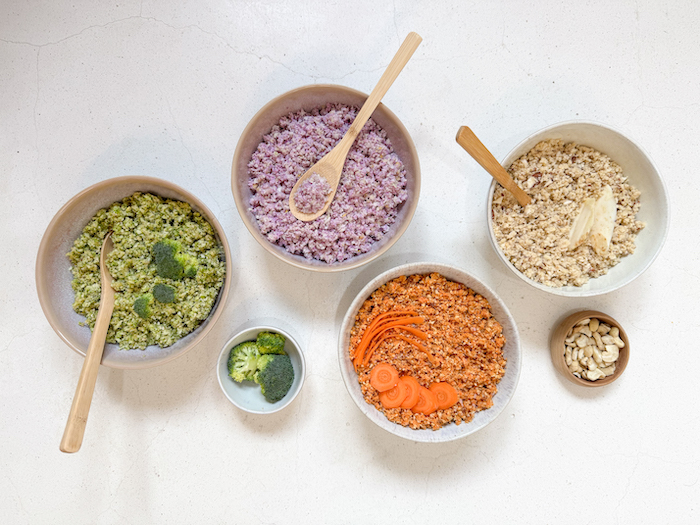
Raw Vegetable Rice Variations
A quick, colorful and nutritious solution for every meal.
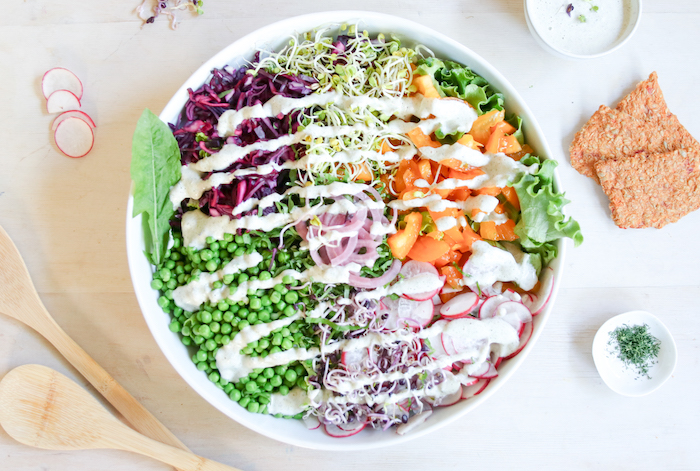
Colorful Summer Salad
A boost that act as powerful antioxidants.
Would you like to join our unique program, based on nutritional sciences and practice-oriented training for gaining a high level of health?
We’re more than happy to inform you about all that our training program offers on our website!







0 Comments